1.
Hybrid Cloud
2.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
3.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
4.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
Q 1 / 90
1.
PaaS
2.
public cloud
3.
private cloud
4.
IaaS
Q 2 / 90
1.
denial-of-service
2.
brute force attacks
3.
malware
4.
buffer overflow
Q 3 / 90
An intrusion detection system (`IDS`) is a device or software application that monitors a network or systems for malicious activity or policy violations.1.
cloud access security broker (CASB)
2.
intrusion prevention system (IPS)
3.
intrusion detection system (IDS)
4.
next generation firewall
Q 4 / 90
1.
SIEM
2.
UTM
3.
protocol analyzer
4.
data sink
Q 5 / 90
1.
code review
2.
code analysis
3.
static analysis
4.
dynamic analysis
Q 6 / 90
1.
gray box testing
2.
integration testing
3.
white box testing
4.
unit testing
Q 7 / 90
1.
none
2.
limited details of server and network infrastructure
3.
all information
4.
limited details of server infrastructure
Q 8 / 90
1.
intrusion prevention system (IPS)
2.
next generation firewall
3.
cloud access security broker (CASB)
4.
intrusion detection system (IDS)
Q 9 / 90
1.
monitoring of normal employee system and data access patterns
2.
applying system and application updates regularly
3.
fault tolerant infrastructure and data redundancy
4.
separation of duties and job rotation
Q 10 / 90
A rainbow table attack is a more efficient and effective way of cracking many hashed passwords, whereas brute-forcing would take much longer and may not complete in a reasonable amount of time.1.
rainbow table attack
2.
pass-the-hash attack
3.
password spray attack
4.
brute force attack
Q 11 / 90
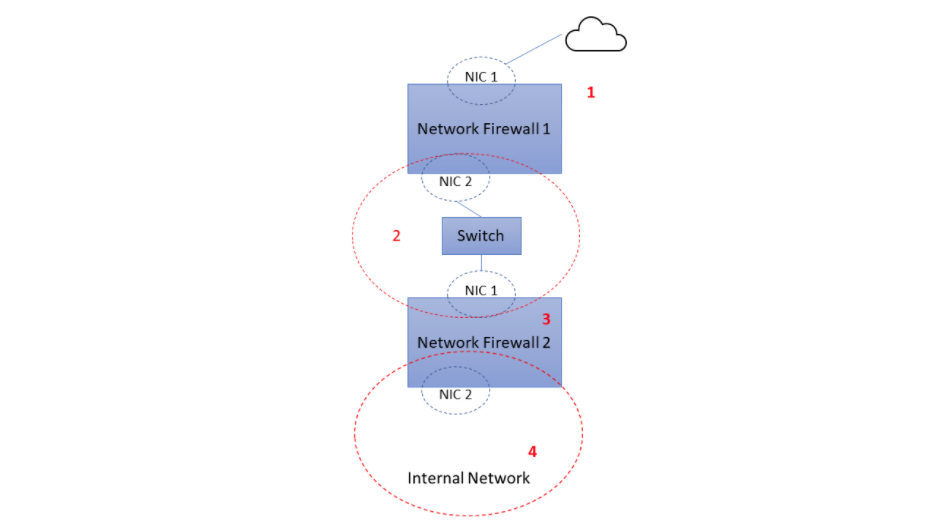1.
4
2.
1
3.
2
4.
3
Q 12 / 90
1.
file hash
2.
asymmetric encryption
3.
digital signature
4.
symmetric encryption
Q 13 / 90
1.
DRP works to keep a business up and running despite a disaster. BCP works to restore the original business capabilities.
2.
BCP works to keep a business up and running despite a disaster. DRP works to restore the original business capabilities.
3.
BCP is part of DRP.
4.
DRP is part of BCP.
Q 14 / 90
1.
non-repudiation
2.
integrity
3.
availability
4.
confidentiality
Q 15 / 90
1.
Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM)
2.
Intrusion Detection and Prevention System (IDPS)
3.
Cloud Workload Protection Platforms (CWPP)
4.
Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASBs)
Q 16 / 90
1.
Compression
2.
Hashing
3.
Symmetric encryption
4.
Stenography
Q 17 / 90
1.
CCPA
2.
GDPR
3.
NIST Privacy Framework
4.
OSPF
Q 18 / 90
1.
identity and access management (IAM)
2.
privileged account management (PAM)
3.
authentication and authorization
4.
least privilege
Q 19 / 90
1.
preventive control
2.
detective control
3.
directive control
4.
corrective control
Q 20 / 90
1.
grayout
2.
blackout
3.
brownout
4.
whiteout
Q 21 / 90
1.
Security Information Event Management (SIEM)
2.
Extended Detection and Response (XDR)
3.
next generation firewall (NGFW)
4.
Cloud App Security Broker (CASB)
Q 22 / 90
1.
TRIKE
2.
TOGAF
3.
STRIDE
4.
MITRE ATT&CK
Q 23 / 90
#### Which strategy should you choose?1.
dynamic application security testing
2.
unit testing
3.
white box testing
4.
static application security testing
Q 24 / 90
1.
Mobile Device Management (MDM)
2.
Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
3.
Intrusion Detection and Prevention System (IDPS)
4.
cloud access security broker (CASB)
Q 25 / 90
**Explaintion**: The formula for asymmetric encryption is `2n`; where `n` is the number of communicating parties.1.
200
2.
400
3.
100
4.
300
Q 26 / 90
**Explaintion**: The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (`PCI DSS`) is the global card industry security standard that is **required of all entities** that store, process, or transmit cardholder data, including financial institutions, online retailers and service providers.1.
Federal Information Security Managment Act (FISMA)
2.
Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI-DSS)
3.
General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
4.
International Organization for Standardization and Internation Electronical Commission (ISO/IEC 27018)
Q 27 / 90
**Explaination**: The Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (`CVE`) system provides a reference-method for publicly known information-security vulnerabilities and exposures.1.
Common event format
2.
common weakness enumeration
3.
common vulnerabilties and exposures
4.
common vulnerability scoring system
Q 28 / 90
**Explanation**: A `protocol analyzer` is a tool used to capture and analyze signals and data traffic over a communication channel.1.
log server
2.
network scanner
3.
firewall
4.
protocol analyzer
Q 29 / 90
**Explaination**: An `Inference Attack` is a data mining technique performed by analyzing data in order to illegitimately gain knowledge about a subject or database. A subject's sensitive information can be considered as leaked if an adversary can infer its real value with a high confidence. **Source**: ([Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Inference_attack)).1.
aggregation
2.
inference
3.
SQL injection
4.
cross-origin resouce sharing
Q 30 / 90
1.
Zero Trust Security
2.
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
3.
authorization
4.
Single Sign-On
Q 31 / 90
1.
processor
2.
object
3.
subject
4.
controller
Q 32 / 90
**Explaination**: zero trust assumes that the system will be breached and designs security as if there is no perimeter. Hence, don’t trust anything by default.1.
use least privilege access
2.
verify explicitly
3.
trust but verify
4.
assume breach
Q 33 / 90
1.
ARP spoofing
2.
pharming attacks
3.
cross-site scripting (XSS)
4.
DNS poisoning
Q 34 / 90
1.
IDS
2.
SIEM
3.
packet sniffer
4.
IPS
Q 35 / 90
1.
`SELECT * FROM users WHERE username = " AND 1=1--'`
2.
`SELECT * FROM users WHERE username = " AND 1!=1--'`
3.
`SELECT * FROM users WHERE username = " OR 1=1--'`
4.
`SELECT * FROM users WHERE username = " OR 1!=1--'`
Q 36 / 90
1.
static analysis
2.
black box testing
3.
dynamic analysis
4.
penetration testing
Q 37 / 90
nmap is a port scanner [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nmap](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nmap) wireshark is a traffic analyzer snort is an IDS autopsy is for forensic analysis1.
Autopsy
2.
Snort
3.
Nmap
4.
Wireshark
Q 38 / 90
1.
Evaluate the features of available DLP products to determine which best meet your organizations's needs.
2.
Examine the flow of sensitive data in your organization to better understand usage patterns.
3.
Conduct an inventory of all the data in your organization to establish classifications based on sensitivity.
4.
Conduct a risk assessment to determine the best data labeling strategy for your organization.
Q 39 / 90
1.
virus
2.
worm
3.
rootkit
4.
Trojan horse
Q 40 / 90
1.
encryption
2.
a metropolitan area network
3.
a virtual local area network
4.
a wide area network
Q 41 / 90
1.
authentication
2.
Single Sign-On
3.
authorization
4.
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
Q 42 / 90
1.
SQL injection
2.
dictionary attack
3.
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS)
4.
rainbow table attack
Q 43 / 90
1.
risk mitigation
2.
threat assessment
3.
risk management
4.
enumeration
Q 44 / 90
1.
man-in-the-middle attack
2.
back door
3.
logic bomb
4.
virus
Q 45 / 90
1.
Extended Detection and Responde (XDR)
2.
Security Information Event Management (SIEM)
3.
Intrusion Detection and Prevention System (IDPS)
4.
Mobile Device Management (MDM)
Q 46 / 90
1.
file permissions
2.
buffer overflow
3.
zero-day vulnerability
4.
cross-site scripting
Q 47 / 90
1.
It identifies regulatory compliance requirements.
2.
It prioritizes IT budget expenditures.
3.
It quantifies the potential cost of a data breach.
4.
It establishes the value of data to the organization.
Q 48 / 90
1.
Cloud Workload Protection Platforms (CWPP)
2.
Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM)
3.
Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASBs)
4.
Intrusion Detection and Prevention System (IDPS)
Q 49 / 90
1.
identification
2.
authorization
3.
accounting
4.
authentication
Q 50 / 90
1.
Eradication / Remediation
2.
Certification
3.
Reporting
4.
Lessons Learned
Q 51 / 90
1.
dynamic analysis
2.
static analysis
3.
penetration testing
4.
black box testing
Q 52 / 90
1.
asymmetric
2.
symmetric
3.
hashing
4.
all of these answers
Q 53 / 90
1.
Reporting
2.
Recovery
3.
Eradiction / Remediation
4.
Lessons Learned
Q 54 / 90
1.
C
2.
Java
3.
Ruby
4.
Python
Q 55 / 90
1.
risk acceptance, risk mitigation, risk containment, and risk qualification
2.
risk avoidance, risk transference, risk containment, and risk quantification
3.
risk avoidance, risk mitigation, risk containment, and risk acceptance
4.
risk avoidance, risk transference, risk mitigation, and risk acceptance
Q 56 / 90
1.
asymmetric
2.
both symmetric and asymmetric
3.
neither symmetric or asymmetric
4.
symmetric
Q 57 / 90
1.
trojan
2.
keystroke collector
3.
typethief
4.
keylogger
Q 58 / 90
1.
by destroying them
2.
by encrypting them
3.
by stealing them
4.
by selling them
Q 59 / 90
1.
It has become a money mule.
2.
It has become a zombie.
3.
It has become a bastion host.
4.
It has become a botnet.
Q 60 / 90
1.
C2M2
2.
NIST SP 800-37
3.
ISO/IEC 27001
4.
COBIT
Q 61 / 90
1.
a risk management framework
2.
a guide to risk assessments
3.
a guideline for vulnerability testing
4.
a step-by-step guide for performing business impact analyses
5.
undefined
Q 62 / 90
1.
duqu
2.
agent BTZ
3.
stuxnet
4.
flame
Q 63 / 90
1.
in the risk assessment documentation
2.
in the risk register
3.
in the business impact ledger
4.
in the Orange Book
Q 64 / 90
1.
disconnection from the network
2.
early containment
3.
continuation of monitoring for other incidents
4.
eradication of the issues
Q 65 / 90
1.
fire and ice exploits
2.
meltdown and spectre exploits
3.
Intel and STMicro CPU exploits
4.
super microboard and Apple iPhone exploits
Q 66 / 90
1.
40 percent
2.
60 percent
3.
85 percent
4.
100 percent
Q 67 / 90
1.
This could be a specific program being run by your accounting department.
2.
This is an in-progress attack and should be reported immediately
3.
This is normal operation for your business.
4.
This could be a precursor to an attack.
Q 68 / 90
1.
annual
2.
biannually
3.
bimonthly
4.
monthly
Q 69 / 90
1.
From an incident response committee to oversee any incidents that may occur.
2.
Get preauthorized to take unilateral action and make or direct emergency changes.
3.
Bring management in as leadership on the incident response team.
4.
Assign a head of the emergency response team who has the correct authority
Q 70 / 90
1.
ISO 27001
2.
NIST SP 800-54
3.
ISO 27002
4.
NIST SP 751-51
Q 71 / 90
1.
Forum of Incident Response and Security Teams
2.
Crest UK Response Teams
3.
Community of Computer Incident Response Teams
4.
NIST Special Publication 800-61 Response Teams
Q 72 / 90
1.
inherent risk
2.
residual risk
3.
applied risk
4.
leftover risk
Q 73 / 90
1.
risk mitigation
2.
risk acceptance
3.
risk avoidance
4.
risk transfer
Q 74 / 90
1.
common criteria
2.
risk management certification board
3.
OWASP security evaluation
4.
ISO 27000
Q 75 / 90
1.
IoT ISACA
2.
IoT Security Foundation
3.
OWASP
4.
GSMA
Q 76 / 90
1.
ISO 27001
2.
ISO 27017
3.
cloud security guidelines
4.
cloud controls matrix
Q 77 / 90
1.
It is versatile, accurate, and operates at a very high speed.
2.
It is tamper-proof, can always be invoked, and must be small enough to test.
3.
It is restricted, confidential, and top secret
Q 78 / 90
1.
Identify the key business outcomes.
2.
Understand the threats and vulnerabilities.
3.
Conduct a risk assessment.
4.
Analyze and prioritize gaps to create the action plan.
Q 79 / 90
1.
the ISACA Cypersecurity Framework
2.
the COBIT Cypersecurity Framework
3.
the ISC2 Cypersecurity Framework
4.
the NIST Cypersecurity Framework
Q 80 / 90
1.
a salami attack
2.
a DoS (Denial of Service) attack
3.
a DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) attack
4.
a botnet attack
Q 81 / 90
1.
an increased business liability in the event of a data breach
2.
an increased consumer liability in the event of a data breach
3.
a decreased consumer liability in the event of a data breach
4.
a decreased business liability in the event of a data breach
Q 82 / 90
1.
FedRAMP
2.
GDPR
3.
PCI-DSS
4.
HIPAA
Q 83 / 90
1.
undefinedQ 84 / 90
1.
DevSecOps requires the inclusion of cybersecurity engineers in the CI/CD process of DevOps.
2.
DevSecOps slows down the CI/CD process of DevOps.
3.
DevSecOps places security controls in the CI/CD process of DevOps.
4.
DevSecOps lets cybersecurity engineers dictate the CI/CD process of DevOps.
Q 85 / 90
1.
always
2.
only when assessing regulatory compliance
3.
only if following the Agile model
4.
never
Q 86 / 90
Control of security required for regulatory compliance Legacy application and database support Scalability to meet seasonal increases in demand Which cloud model is the best option for these requirements?1.
government cloud
2.
public cloud
3.
hybrid cloud
4.
private cloud
Q 87 / 90
1.
Give up on the current target network and move on to the next one.
2.
Switch to another network scanning tool. Resort to more resource-intensive probing, like launching random attacks to all open ports.
3.
Turn on the stealth mode in your network scanning tool. Check whether you missed any other active ports associated with web servers.
4.
Turn on additional options in your network scanning tool to further investigate the details (type and version) of applications running on the rest of the active ports.
Q 88 / 90
What are the primary goals of the digital signature in this scenario? (Choose the best answer.)1.
integrity and non-repudiation
2.
privacy and non-repudiation
3.
privacy and confidentiality
4.
integrity and privacy
Q 89 / 90
1.
MD5
2.
Caesar cipher
3.
symmetric-key encryption
4.
asymmetric-key encryption
Q 90 / 90